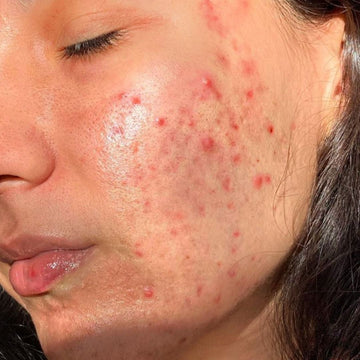
Understanding Acne Vulgaris
What is Acne Vulgaris?
Acne vulgaris is a common skin condition involving inflammation, often perceived as a temporary issue in adolescence but persisting into adulthood. Approximately 90% of teenagers experience acne, and around 50% continue to have symptoms as adults. Recent studies indicate a growing prevalence of acne in children, possibly due to the onset of puberty.
Definition of Acne Vulgaris
Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder primarily affecting the pilosebaceous units—the hair follicles and oil glands—resulting in comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. It commonly occurs on the face but can appear on the chest, back, shoulders, and other body areas.
What Causes Acne Vulgaris?
Understanding the underlying causes of acne vulgaris is crucial for effective treatment. Several key elements contribute to its development:
1.Hormonal Imbalances: Increased androgen levels stimulate sebaceous glands, leading to excess sebum production and clogged hair follicles.2.Excess Sebum Production: Overproduction of sebum can result in clogged follicles, trapping bacteria and dead skin cells and causing acne formation.
3.Bacterial Influence: Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) in acne-prone individuals contributes to inflammation when follicles are clogged.
4.Follicular Hyperkeratinization: Abnormal shedding of skin cells within hair follicles contributes to the accumulation of plugs, fostering bacteria growth.
5.Inflammation: Inflammatory response triggered by clogged follicles and bacterial proliferation leads to redness, swelling, and acne lesions.
6.Genetic Predisposition: Genetics may influence susceptibility to acne, with family history impacting factors like sebum production and immune response.
7.External Factors: Diet, environmental factors, stress, and certain cosmetic products may exacerbate existing acne or trigger flare-ups.
Pathophysiology of Acne Vulgaris
Acne vulgaris involves complex biological processes within the skin. Understanding its pathophysiology sheds light on underlying mechanisms:
1.Sebaceous Gland Hyperactivity and Sebum Production: Overactivity of sebaceous glands, driven by hormonal imbalances, contributes to excess sebum production and acne lesions.2.Follicular Hyperkeratinization and Comedone Formation: Abnormal shedding of skin cells leads to the formation of plugs or comedones, including blackheads and whiteheads.
3.Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) Bacterial Infection: P. acnes multiplies within hair follicles, triggering an immune response and inflammation.
4.Inflammation and Immune Response: Inflammatory mediators released in response to clogged follicles lead to redness, swelling, and various acne lesions.
5.Hormonal Influence on Acne Vulgaris: Hormonal imbalances, especially increased androgens, stimulate sebaceous glands, contributing to acne development.
6.Genetic Predisposition: Genetics may influence susceptibility to acne vulgaris, impacting factors such as sebum production and immune response.
Types of Acne Vulgaris
Acne vulgaris manifests in various forms. Understanding the types is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment:
a.Comedonal Acne: Characterized by comedones—non-inflammatory lesions like blackheads and whiteheads.
b.Inflammatory Acne: Presents as red, inflamed lesions, including papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
Signs and Symptoms of Acne Vulgaris
The signs and symptoms vary in severity but commonly include comedones, inflammatory lesions, nodules, cysts, redness, swelling, oily skin, and scarring.
Management of Acne Vulgaris
Effective management involves a comprehensive approach:
1.Topical Medications: Retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, topical antibiotics, and azelaic acid target acne lesions.2.Oral Medications: Antibiotics, hormonal therapy, and isotretinoin are prescribed for moderate to severe acne.
3.Professional Procedures: Chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser or light therapies, and corticosteroid injections may be performed.
4.Skincare Practices: Establishing a consistent skincare routine with non-comedogenic products is crucial.
5.Lifestyle Modifications: Dietary changes, stress management, and avoiding skin irritants support acne management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1.Is acne vulgaris the same as acne?Yes, both terms are often used interchangeably.
2.Can acne vulgaris be cured?
While not curable, it can be effectively managed with appropriate treatments.
3.Can certain foods worsen acne?
Some individuals may experience worsened acne with certain foods.
4.How long does it take to see results from acne treatments?
Improvement timelines vary, taking weeks to months for noticeable results.
5.Should I pop my pimples?
Popping pimples is generally not recommended to avoid further inflammation and scarring.
6.Can stress worsen acne?
Yes, stress can potentially worsen acne due to hormonal changes.
7.Are there natural remedies for acne?
Natural remedies may provide mild relief but are not substitutes for evidence-based medical treatments.
8.How long does it take for acne vulgaris to clear up?
Duration varies based on severity, ranging from weeks to months.
9.Can stress worsen acne vulgaris?
While not a direct cause, stress can exacerbate existing acne due to hormonal changes.